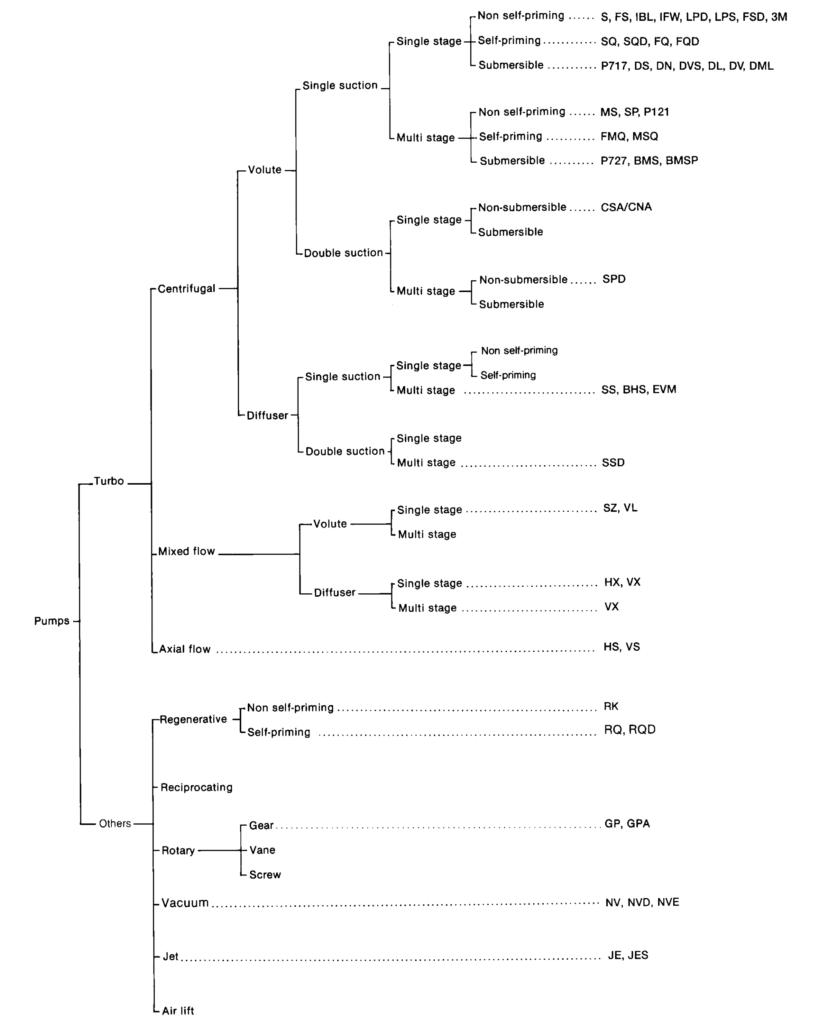
CLASSIFICATION OF TURBO PUMPS
Turbo pumps are loosely grouped into the following three types.
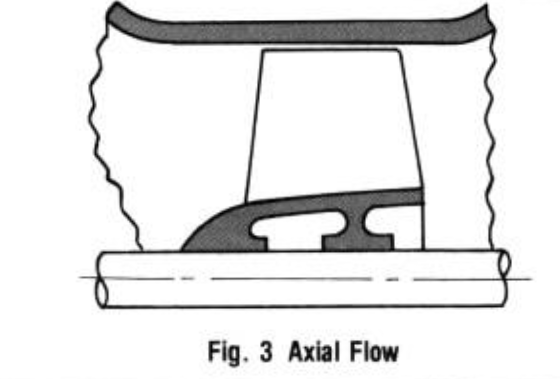
1- Centrifugal Pump
Pump head caused primarily by the centrifugal force of impeller rotation. This type pump is widely used for its high head capability.
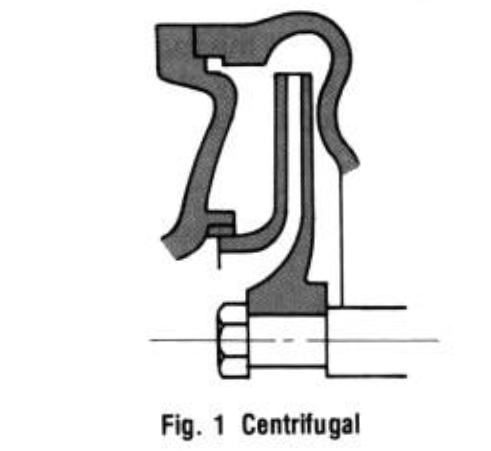
2-Mixed Flow Pump
Here pump head is derived partly from rotation of the impeller, partly from impeller lift.
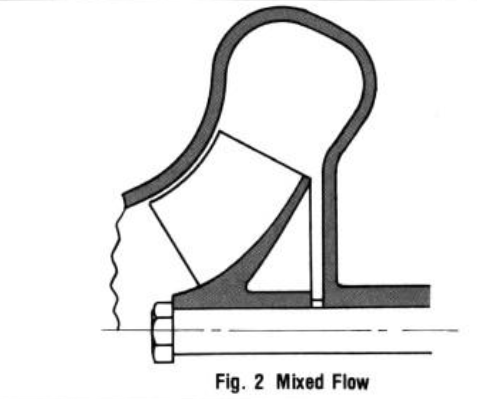
3-Axial Flow Pump
Head produced by this pump is primarily a result of impeller action on water. It is used extensively when a large flow with low head is required.
These three kinds of pumps are also classified according to types of casing and impellers.
CASING
Volute Pump & Diffuser Pump:
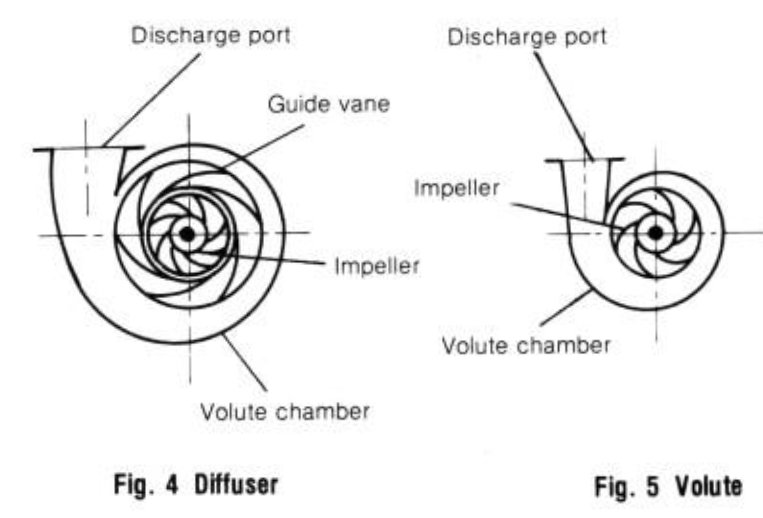
Water flows from impeller at high speed, which must be efficiently converted into pressure. In a diffuser pump, this conversion is performed by a guide vane installed in contact with the impeller. In a volute pump, conversion is by a volute casing not provided with a guide vane.
Because of its high efficiency in handling a wide flow of water, simplicity of construction and compactness a volute pump is universally used, except for such special use, as with a deep well.
SUCTION TYPES
Single Suction & Double Suction:
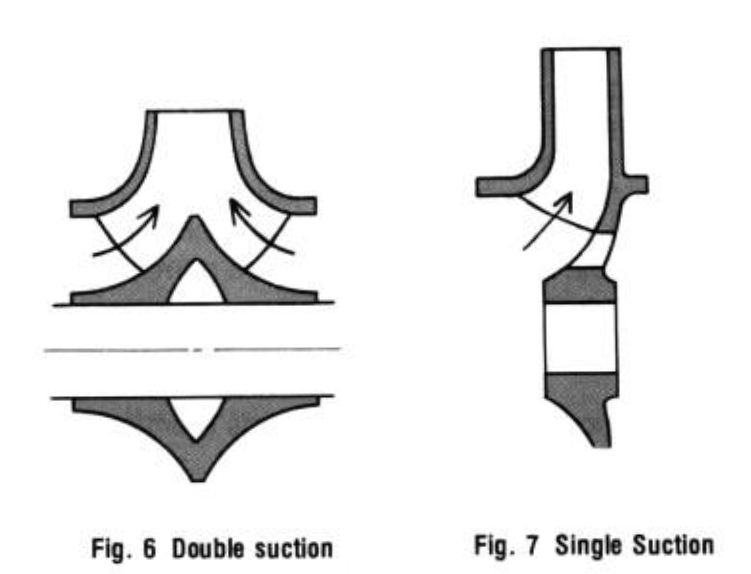
When single suction is insufficient to move a large volume of water, two impellers are used back to back, and suction occurs on both sides. This, then, is the double suction type. Double suction improves efficiency, and the axial thrust is, in theory, balanced. However, because of structural complications, double suction is not used in other volute type pumps.
MULTI-STAGES
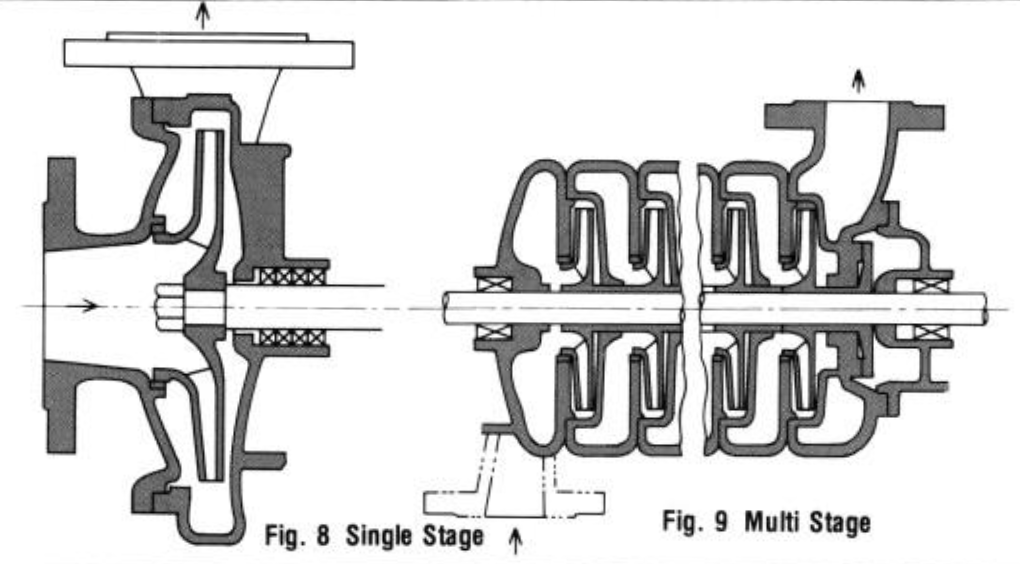
When a single impeller fails to produce the required head, several impellers are arranged on as many stages on the principle of series operation of pumps. Most high head pumps are rnultistage type.
NON-SELF-PRIMING & SELF-PRIMING PUMPS
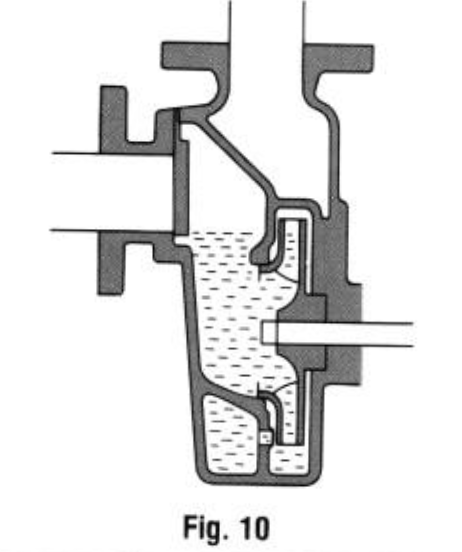
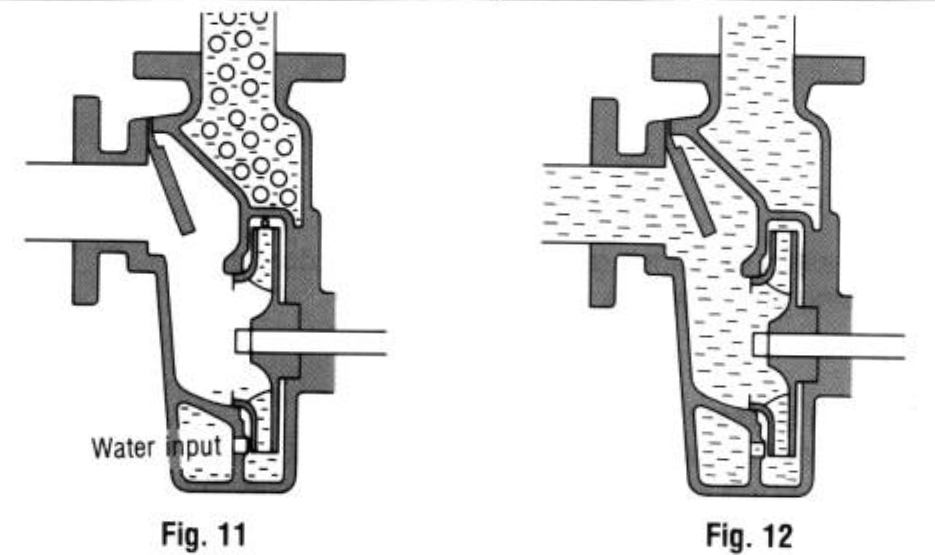
It is necessary to prime a conventional pump prior to operation to create a water channel from the pump through the suction piping. A self-priming pump can be started without the need for this drudgery, if there is water
in the pump, without the need for water in the suction pipe. Self-priming pumps work as follows:
i) Prior to operation, water is in the casing and the impeller is immersed in water
ii) With the start of operation, the impeller creates a vacuum in the pump, and air in the suction pipe is gradually drawn into the pump On the outlet side. air alone is discharged and water circulates within the impeller
iii) With the complete removal of air from the suction pipe. the pump commences regular watering
SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS
Submersible pumps have enjoyed fast progress in recent years because:
1) No installation space is necessary.
2) Priming is not required.
3) There is no worry about cavitation.
Another reason for the popularity of submersible pumps is the new reliability of submersible motors and their mechanical seals. plus the availability of these pumps at moderate cos
OTHER PUMP
In addition to the various types of turbo pumps mentioned
above. there are others such as regenerative. reciprocating. rotary. vacuum, jet and air lift pumps. These pumps. however. have special applications. Most widely used among pumps are turbo pumps, and. particularly, centrifugal volute pumps

Leave a Reply