Direct start
Direct starting is the simplest method of starting and is obtained by connecting the motor’s rated voltage to the stator. In general, this is used for small motors which can run up to speed in short time.
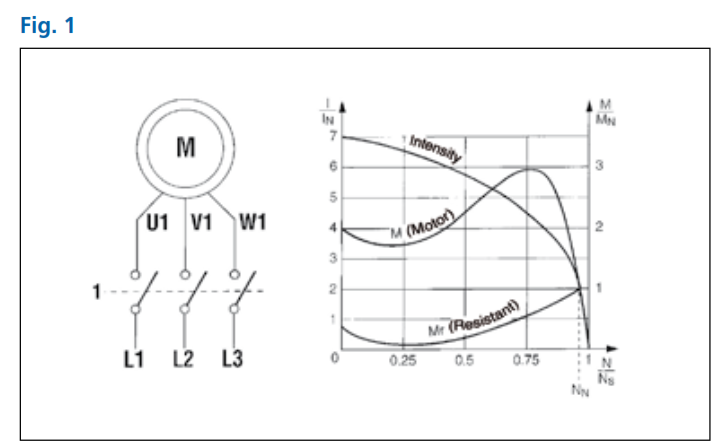
Fig. 1 shows the direct starting procedure, obtained by closing
connections “1”.
The main disadvantages, as can be seen in the figure, consist in a high current absorption by the rotor when starting, and hence a high current demand from the power supply by the stator, which causes sudden voltage drops and disturbs the mains itself.
The advantages, along with the simplicity of the configuration, consist in good starting torque and minimum starting time.
Star-Delta start (Y – Δ)
This method is used for motor which are powered, when run up to speed, with a delta connection, indicated with the letter Δ.
It consists in starting the motor with a star (Y) winding and then, once the motor has started, switching the windings to the delta configuration (Δ) when the motor is close to running speed.
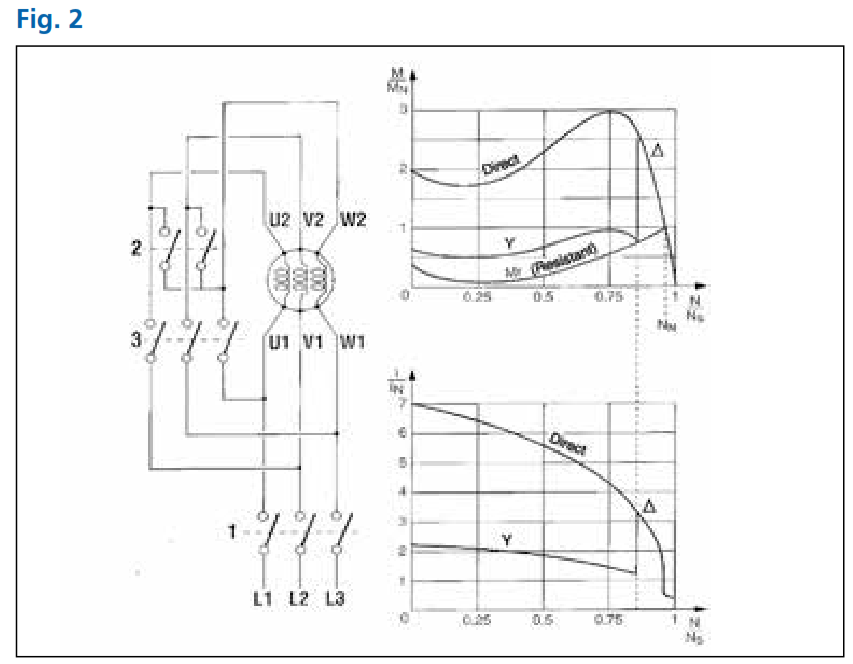
As can be seen in Fig. 2, connections 2 are closed and connections 3 left open, to configure the windings in a star arrangement, then contacts 1 are closed the motor starts in a star configuration. In this way, the motor absorbs 1/ of the line current compared to the absorption in the delta configuration. The starting torque is also reduced by a factor of 3 compared to delta Δ starting.
When a certain set speed is reached, connections 2 are opened and
connections 3 are closed, thus switching the windings into a delta
configuration. The torque rises as does the current absorption, in
comparison with the Y configuration.
This method is generally used for motors of power from 7 to 50 kW.

Leave a Reply